Filing your Income Tax Return (ITR) can feel like navigating a maze—especially when you’re faced with multiple ITR forms and no clue which one applies to your situation. Whether you’re a salaried employee, freelancer, business owner, or investor, choosing the correct ITR form is crucial for accurate filing and avoiding penalties.
In this blog, we’ll break down the various ITR forms and help you figure out which one is right for you.
What is ITR
An Income Tax Return (ITR) is a form where you tell the government how much money you made and how much tax you need to pay (or already paid) on it.
What is an ITR Form?
An ITR form is a document used to file income tax returns in India. It’s a way for individuals and businesses to report their income, deductions, and taxes paid to the Income Tax Department. The form you use depends on your income source, income amount, and category (individual, HUF, company, etc.)
ITR forms help individuals and businesses report their income from various sources. It allow taxpayers to claim deductions and exemptions. It help taxpayers calculate and pay their tax liability. Filing ITR form is an important legal requirement for taxpayers. It not helps taxpayers to claim tax refunds/pay tax dues but it also acts as a financial record for taxpayers.
Overview of different types of ITR Forms (FY 2024-25 / AY 2025-26)
There are different ITR forms for individuals, HUFs, firms, companies, and other entities. Different forms are used for different types of income, such as business income, salary income, or capital gains. To determine which ITR form is applicable to you following points needs to be considered:
ITR-1 (SAHAJ)
Who should file:
- Resident individuals (not HUF)
- Total income up to ₹50 lakh
- Income sources:
- Salary or pension
- One house property
- Other sources (e.g., interest)
Not applicable if:
- You have capital gains, foreign income/assets, or income from more than one house property.
Ideal for: Salaried individuals with simple income structure.
ITR-2
Who should file:
- Individuals and HUFs not having income from business or profession
- Income sources:
- Salary/pension
- Multiple house properties
- Capital gains
- Foreign assets/income
Ideal for: Investors, NRIs, and those with capital gains or foreign income.
ITR-3
Who should file:
- Individuals and HUFs with income from:
- Proprietorship
- Business or profession
- Presumptive income under Sections 44AD, 44ADA, or 44AE
Also includes: Salary, house property, capital gains, and other sources. Ideal for: Freelancers, consultants, professionals (e.g., doctors, lawyers), business owners
ITR-4 (SUGAM)
Who should file:
- Individuals, HUFs, and firms (other than LLP) opting for presumptive taxation
- Business income under Sec 44AD
- Professional income under Sec 44ADA
Total income limit: Up to ₹50 lakh
Ideal for: Small business owners and professionals who want to file under presumptive income.
ITR-5
Who should file:
- LLPs, Partnership firms, AOPs, BOIs (excluding those required to file ITR-7)
ITR-6
Who should file:
- Companies not claiming exemption under Section 11 (income from property held for charitable or religious purposes)
ITR-7
Who should file:
- Entities required to furnish return under Sections 139(4A) to 139(4F), like:
- Trusts
- Political parties
- Research associations
- Institutions under certain sections
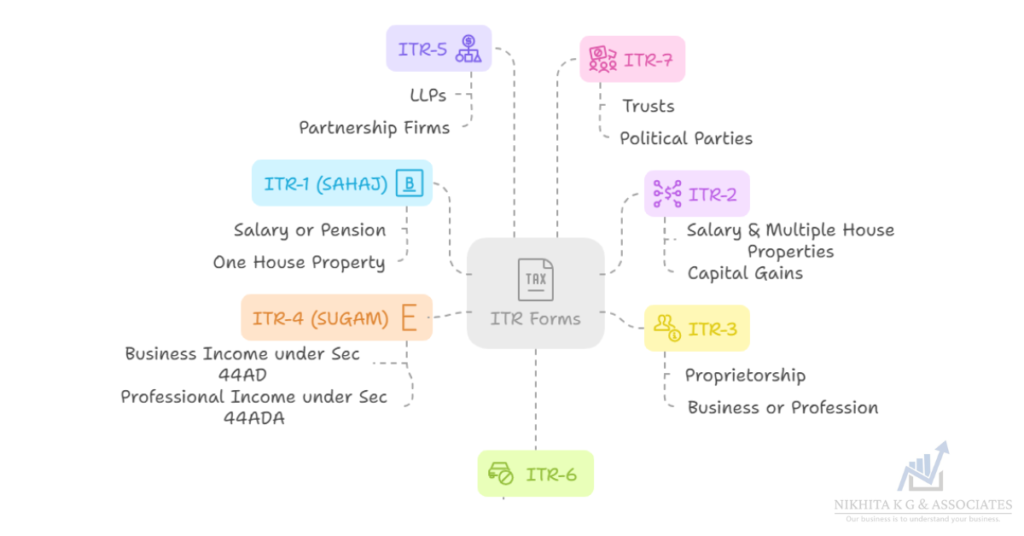
Which ITR Form is Right for You?
As it can be seen from above there are different ITR forms and there applicability depends on many factors (Type of person, Income source etc.) The income tax e-filing portal has a helpful questionnaire that guides you to the correct ITR form. Still, understanding the basics helps ensure you’re compliant and avoid filing the wrong form. You can choose the right ITR form applicable for you through this quick reference guide:
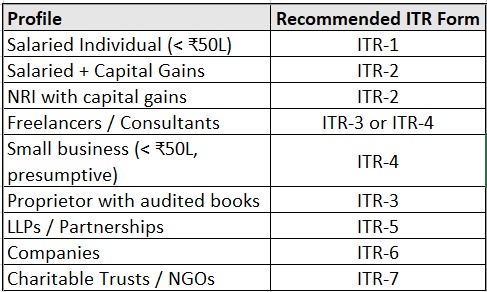
Quick Checklist Before You Choose the Right ITR form
- Are you a resident or NRI?
- Are you an individual or HUF?
- Do you earn only salary or have multiple income sources?
- Do you have income from business or profession?
- Do you own multiple properties?
- Do you have foreign income or assets?
- Are you a director in a company or have investments in unlisted equity shares?
- Are you opting for presumptive taxation?
- Does your income exceed ₹50 lakh?
- Do you require an audit?
Based on your answers to these questions, you can determine which ITR form is applicable to you. It will guide you to the right form for your tax filing needs.
FAQs About ITR Forms
1. What happens if I file the wrong ITR form?
Filing the wrong ITR form may lead to rejection of your return, delayed processing, or even penalties. It’s important to file the correct form to avoid notices from the Income Tax Department.
2. Can salaried individuals file ITR-2 instead of ITR-1?
Yes, salaried individuals with income from capital gains, multiple house properties, or foreign assets/income must file ITR-2 instead of ITR-1.
3. I am a freelancer. Which ITR form should I file?
Freelancers usually file ITR-3 if they maintain regular books of account, or ITR-4 if they opt for presumptive taxation under Section 44ADA.
4. I have rental income from two properties. Which ITR form should I use?
If you have income from more than one house property, you can’t file ITR-1. Based on other factors, ITR-2 or ITR-3 may be applicable.
5. What is presumptive taxation and which ITR form is used for it?
Presumptive taxation allows small taxpayers to declare income at a prescribed rate. ITR-4 (SUGAM) is used by individuals, HUFs, and firms opting for presumptive income under Sections 44AD, 44ADA, or 44AE.
6. Is it mandatory to file ITR even if my income is below ₹2.5 lakh?
No, it’s not mandatory unless you meet certain criteria (like foreign travel, electricity bills, holding foreign assets, etc.). However, filing ITR can be beneficial for loan applications, visa processing, or claiming refunds.
7. Can I revise my ITR if I filed the wrong form?
Yes, you can revise your return within the deadline if you realize that you used the wrong ITR form. Always cross-check before submission.
8. How do I know which ITR form to file?
You can use the questionnaire tool available on the Income Tax e-Filing Portal or refer to the checklist provided in this blog to decide based on your income type, category, and other factors.
9. What if I have foreign income or assets?
If you have foreign income or hold foreign assets, ITR-2 or ITR-3 is applicable depending on whether you have business/professional income.
10. Is it necessary to consult a CA or tax expert to file ITR?
While salaried individuals with simple incomes can file ITR themselves, it’s advisable to consult a tax advisor if you have multiple income sources, capital gains, or business income.
Summary
Filing the right ITR form is not just about compliance it ensures that you claim all eligible deductions, avoid notices, and get your refund (if any) without delays. When in doubt, consult a tax advisor, especially if your income sources are diversified.

